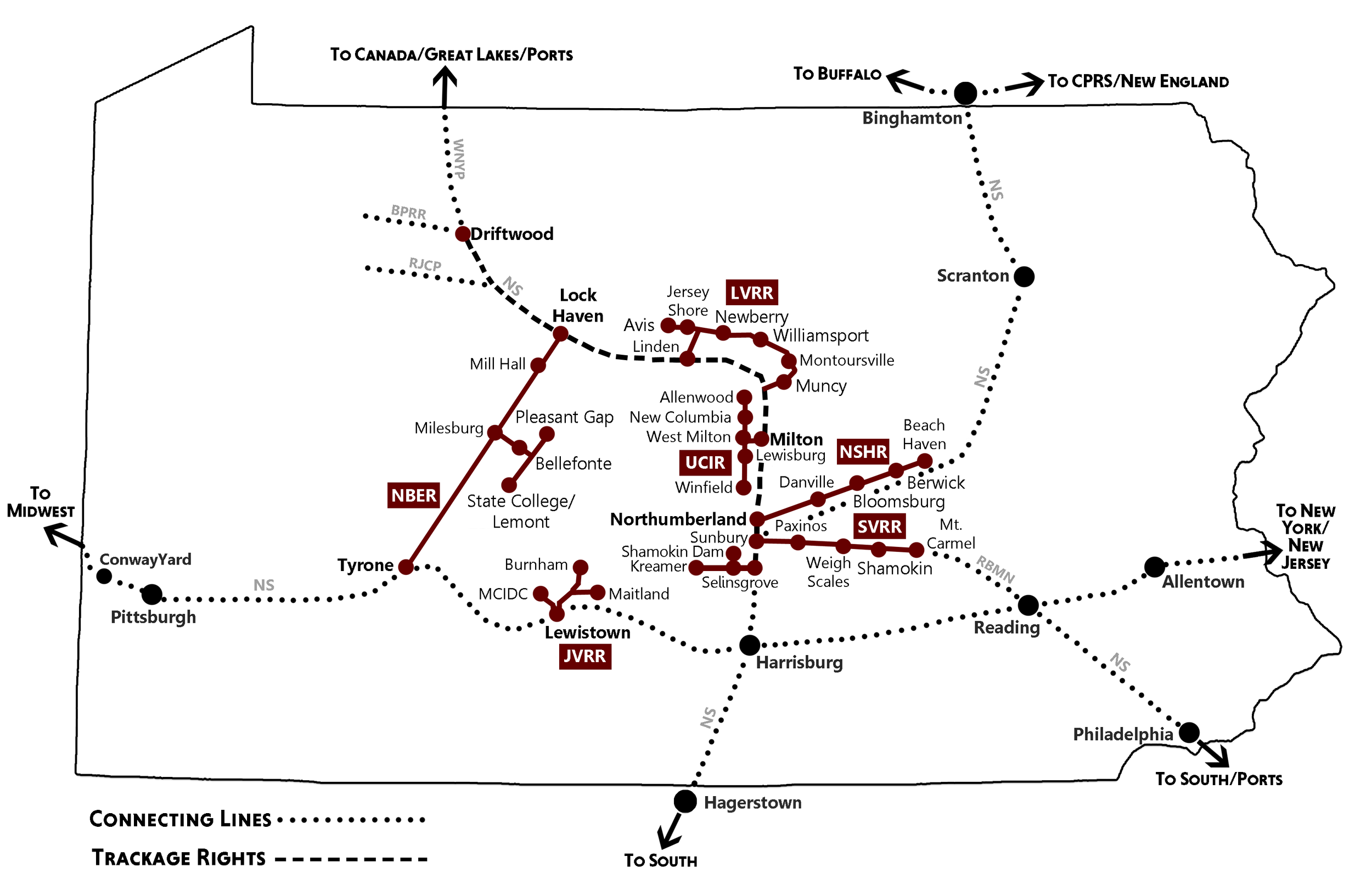
Our Short Line Railroads
It all began in 1984…
North Shore
Serving Customers from Northumberland to Berwick, PA | Since August 1, 1984
Serving Customers from Selinsgrove to Kreamer and Shamokin Dam, PA | Since April 28, 2022
Today, North Shore Railroad is a 49.8 mile short line that interchanges with Norfolk Southern and Canadian Pacific Railway (via NS Haulage) in Northumberland, PA. NSHR handles commodities that vary from grains and plastics to scrap metals and concrete vaults. The infrastructure is owned by SEDA-COG JRA.
NSHR, established August 1, 1984, is a short line serving 40.8 miles of railroad in Northumberland, Danville, Bloomsburg, and Berwick, Pennsylvania, as well as the “Selinsgrove Branch” which is 7.7 miles from Selinsgrove to Kreamer, PA and 1.3 miles from Selinsgrove to Shamokin Dam, PA.
The NSHR line parallels the North Branch of the Susquehanna River and the old North Branch Canal. The line was originally built by Lackawanna & Bloomsburg Railroad (L&B), incorporated in 1852 to serve the coal mines and iron industry between Scranton and Northumberland. The L&B became part of the Delaware Lackawanna & Western Railroad (DL&W) in 1873. DL&W became Erie Lackawanna in 1960 and then Conrail in 1976. Conrail abandoned the middle portion of the line between Hicks Ferry and Kinston, and then sold the western segment to the SEDA-COG Joint Rail Authority (JRA) in 1984. The JRA then contracted with NSHR to operate it.
In 2022, NSHR began operating the NSHR Selinsgrove Branch. The JRA purchased this branch from Norfolk Southern on April 28, 2022. Prior to the sale, Norfolk Southern had been operating the line since 1999, after acquiring it from Conrail. The majority of the line was originally built in 1871, by the Sunbury & Lewistown Railroad, where it was leased to and operated by the Pennsylvania Railroad (PRR).
Nittany & Bald Eagle
Serving Customers from Lock Haven to Tyrone and Bellefonte, PA | Since August 1, 1984
Today, Nittany & Bald Eagle Railroad is a 87.3 mile short line that interchanges with Norfolk Southern in Lock Haven and Tyrone, PA. NBER also interchanges with the Canadian Pacific Railway (via NS haulage) in Lock Haven, PA. The NBER serves the communities of Lock Haven, Tyrone, Bellefonte, Pleasant Gap, and State College. The infrastructure is owned by SEDA-COG JRA.
NBER was established August 1, 1984. The Nittany line dates back to 1857, with the incorporation of the Tyrone & Lock Haven Railroad to serve the coal and iron industries centered around Milesburg and Bellefonte. The railroad was renamed the Bald Eagle Valley Railroad in 1861, and in 1864 was acquired by the Pennsylvania Railroad. Some of the Nittany's trackage was partially abandoned by Conrail in 1982 and 1983. The NBER preserves rail transportation for industry in Blair, Centre, and Clinton Counties. It hauls large quantities of stone and general merchandise, and serves as a bridge line for the movement of coal to power plants. NBER's blue and white colors honor Penn State University.
Shamokin Valley Railroad
Serving Customers from Sunbury to Shamokin, PA | Since November 9, 1988
Today, Shamokin Valley Railroad is a 28.8 mile short line that interchanges with Norfolk Southern and Canadian Pacific Railway (via NS Haulage) in Northumberland, PA, and Reading Blue Mountain and Northern Railroad in Locust Summit, PA. In 2012, PA Rail Transloading, LLC, completed a 660’ long high wall that can accommodate ten railcars for truck to rail transfer of bulk commodities in Shamokin, PA. The infrastructure is owned by SEDA-COG JRA.
The predecessors of SVRR date back to the Danville & Pottsville Railroad, which was incorporated in 1826, and finished construction between Sunbury and Shamokin in 1838. This company became the Philadelphia & Sunbury Railroad in 1851, and in 1858 the line became the Shamokin Valley & Pottsville Railroad (SV&P). The SV&P was leased by the Northern Central Railway in 1883, thence passed to the Pennsylvania Railroad’s control, but continued its separate corporate existence under until acquired by Conrail in 1976. When the line was sold in 1987, the SEDA-COG Joint Rail Authority acquired it to maintain rail service in Northumberland County and the SVRR was incorporated as the operating company. The west 12 miles of the SVRR, between Sunbury and Reed, utilizes the former Reading Company’s alignment (opened 1883 as the Shamokin, Sunbury & Lewisburg Railroad).
Union County Industrial Railroad
Serving Customers from New Columbia to Winfield, PA | Since March 30, 1995
Today, Union County Industrial Railroad is a 18.2 mile short line that interchanges with Norfolk Southern and Canadian Pacific Railway (via NS Haulage) in Northumberland, PA. In December 2013, the completion of the restoration of the White Deer Bridge effectively restored service to Allenwood, PA and, in particular, Great Stream Commons (GSC).
The present UCIR extends from its southern terminus at Winfield, PA, through West Milton to Allenwood, PA. This was Reading Railroad territory. At West Milton, the Reading’s “SS&L” (Shamokin, Sunbury & Lewisburg) line met its “Catawissa Railroad” which continued northward to Williamsport. The line from West Milton, through New Columbia to Newberry Jct at Williamsport, was part of the Reading’s longest and most lucrative haul, from the Port of Philadelphia to friendly western connections. The antecedent of this line was the Catawissa, Williamsport & Erie Railroad (CW&E RR), which had been incorporated in 1829 as the Little Schuylkill & Susquehanna Railroad, but never reached Catawissa. The new CW&E RR in 1854 finished construction of the line as far west as Milton, Pa, where a connection was made with the Sunbury & Erie Railroad. For the next 15 years, Williamsport was reached by operating its trains over the Sunbury & Erie. By 1860, the CW&E RR had fallen under the influence of the Philadelphia & Reading Railroad, which reorganized the line as simply the Catawissa Railroad. This company continued its separate existence until 1953, when it was merged into its parent. With the formation of Conrail in 1976, Williamsport-bound traffic was moved to the former Pennsylvania Railroad (PRR) Buffalo Main and the “Catawissa route” was in large part abandoned. The remaining trackage was sold by Conrail in 1995 to private parties, at which time the UCIR was formed to operate the line.
Lycoming Valley Railroad
Serving Customers from Montgomery to Avis, PA | Since August 15, 1996
Today, Lycoming Valley Railroad is a 50 mile short line that interchanges with Norfolk Southern and Canadian Pacific Railway (via NS Haulage) in Northumberland, PA. LVRR is the largest short line on the North Shore Railroad Company system. The infrastructure is owned by SEDA-COG JRA.
Vast stands of timber and nearby coal deposits brought 3 early railroads to the Williamsport area. In December, 1854, the Sunbury & Erie Railroad, a Pennsylvania Railroad predecessor, built northward through Williamsport. The Catawissa, Williamsport & Erie Railroad, a Reading Railroad predecessor, ran its trains to Williamsport over Sunbury & Erie from 1854 until its own line was constructed 1871. The New York Central Railroad presence in the Valley dates from 1883, when its Pine Creek Railroad opened between Wellsboro and Newberry, to haul coal. All these routes were merged into Conrail in 1976. Purchased by the SEDA-COG Joint Rail Authority, they have been operated by the Lycoming Valley Railroad Company since August 15, 1996.
Juniata Valley Railroad
Serving Customers from Lewistown to Burnham, PA | Since August 19, 1996
Today, Juniata Valley Railroad is an 18.5 mile short line that interchanges with Norfolk Southern in Lewistown, PA. JVRR delivers commodities that vary from scrap and finished metals to plastics, fertilizer and pulp. The infrastructure is owned by SEDA-COG JRA.
The JVRR was incorporated in 1996 to assume from Conrail the operation of the three branch lines radiating out of Lewistown. These lines include remnants of the former railroads extending to Selinsgrove and to Milroy, and the branch to the West Mifflin Industrial Park. The Pennsylvania Railroad (PRR) had been incorporated in 1846, to construct from Harrisburg to Pittsburgh. Three years later (1949) Lewistown became its first western terminus and industry quickly developed due to the proximity of the Juniata iron ores. The Freedom Forge at Burnham/Yeagertown had been producing pig iron from these ores since 1795, and was acquired by Andrew Carnegie in 1865. The Mifflin & Centre County Railroad (M&C RR) was projected to build northward through this iron belt, from Lewistown to Milesburg, in 1860. Construction began in 1863, and by 1865 the line extended only 12 miles to Milroy, there being no favorable route northward over Seven Mountains to Milesburg. The PRR leased the M&CC RR in May 1865, and for years handled enormous traffic to and from Burnham Steel Company, successor to the Freedom Forge. The north end of the line was abandoned in segments between 1976 and 1980. Entrepreneurs also projected a line eastward from Lewistown to the Susquehanna River at Selinsgrove and Port Trevorton, incorporating the Middle Creek Railroad in 1865. Despite having constructed some roadbed, this line was waning by 1870. It was reincorporated as the Sunbury & Lewistown Railroad in 1870, opened from Lewistown to Selinsgrove, 43.5 miles, on December 1, 1871, and immediately leased by the PRR. But the traffic was rural and the little line was foreclosed in 1874. It was reincorporated again in 1874 and immediately leased “by PRR interests.” Under PRR control, it served as an important shortcut for moving Wilkes-Barre anthracite westward, avoiding Harrisburg, and for moving perishables to New York markets via interchange with the Lehigh Valley Railroad at Mt. Carmel, avoiding both Harrisburg and Philadelphia. With the industrial decline of the 1950s, the middle of the line was taken up beginning in 1957. Conrail operated the line from 1976 until the JVRR became the operator on August 19, 1996.